📕 subnode [[@bbchase/ospf]]
in 📚 node [[ospf]]
- Open Shortest Path First
- References
- [[Routing Protocol]]
-
History
- standardized in 1989
- Developed largely by DEC
-
Terms
- LSDB (Link State Database): A database that stores LSAs. This is how OSPF builds a picture of the network. A network topology map.
- LSA (Link State Advertisement): A data structure that describes part of the network.
- DBD or DDP (Database Description packet): A list of LSAs that a router has. This packet does not contain LSAs, just the headers. This is sent to a neighbor so it can figure out which LSAs to request.
- LSU (Link State Update): A packet containing LSAs.
- LSAck (Link State Acknowledgement): Confirms receipt of an LSU.
- LSR (Link State Request): A packet which requests a list of LSAs that the router has found are missing or out of date based on its neighbor's Dababase Description (DBD).
- Neighbors: A relationship between routers on the same data link that, once established, allows them to exchange their LSDBs.
-
OSPF Areas
- 32-bit number, can be decimal or dotted-decimal
-
Area 0 (0.0.0.0)
- Backbone area
- All areas must connect to Area 0
- Stub Area
- Not-so-stubby Area (NSSA)
- Totally Stubby Area
- Totally Stubby NSSA
- Transit Area
-
OSPF Router Types
- IR (Internal Router)
- BR (Backbone Router)
- ABR (Area Border Router)
- ASBR (Autonomous System Border Router)
-
OSPF Router Attributes
- DR (Designated Router)
- BDR (Backup Designated Router)
-
LSA Types
-
Type 1 - Router LSA
- LSA Originator:: All routers
- LSA Scope:: Same area
-
Advertises::
- Itself
- Links in the same area
-
Type 2 - Network LSA
- LSA Originator:: DR
- LSA Scope:: Same Area
-
Advertises::
- Routers on the same segment
-
Type 3 - Summary LSA
- LSA Originator:: ABR
- LSA Scope:: Connected areas
-
Advertises::
- Prefixes and metrics for connected area
- Can optionally do route summarization
-
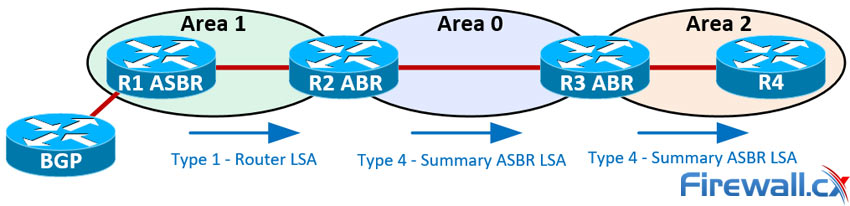
Type 4 - ASBR-Summary LSA
- LSA Originator:: ABR
- LSA Scope:: All except stub and NSSA
-
Advertises::
- Location of ASBRs to other areas. ASBRs flood Type 1 LSA, which are not transmitted to other areas. When an ABR receives a Type 1 LSA form an ASBR, it creates a Type 4 LSA to send to other areas.
-
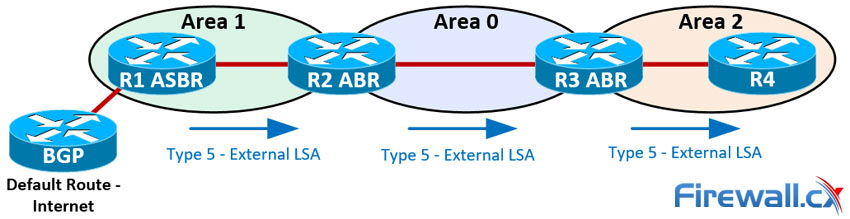
Type 5 - External LSA
- LSA Originator:: ASBR
- LSA Scope:: All except stub and NSSA
-
Advertises::
- Information from other routing processes
-
Type 6 - Group Membership LSA
- Meant for Multicast OSPF, Not widely used.
-
Type 7 - NSSA External LSA
- LSA Originator:: ASBR in a NSSA
- LSA Scope:: Same area
-
Advertises::
- Mask for a Type 5 LSA in an area that blocks Type 5 LSAs. This is needed when an ASBR is inside a NSSA. When the Type 7 reaches the ABR, it's translated to a Type 5
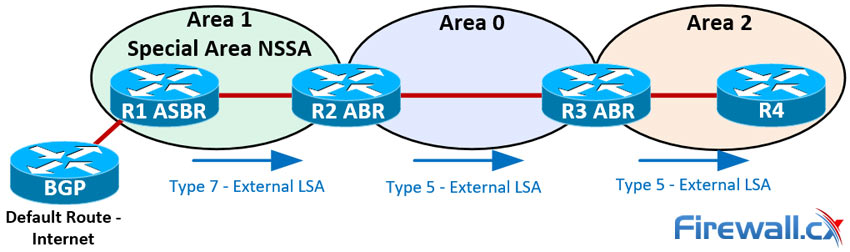
- Pick this up later: http://www.firewall.cx/networking-topics/routing/ospf-routing-protocol/1178-ospf-lsa-types-explained.html
-
Type 8 - External Attributes LSA
- LSA Originator::
- LSA Scope::
- Advertises::
-
Type 9 - Link Scope Opaque LSA
- LSA Originator::
- LSA Scope::
- Advertises::
-
Type 10 - Area Scope Opaque LSA
- LSA Originator::
- LSA Scope::
- Advertises::
-
Type 11 - AS Scope Opaque LSA
- LSA Originator::
- LSA Scope::
- Advertises::
-
Type 1 - Router LSA
- Related
📖 stoas
- public document at doc.anagora.org/ospf
- video call at meet.jit.si/ospf